New Drug Approvals 2011 - Pt. XXX - Aflibercept (EyleaTM)

On November 18th 2011, the FDA approved Aflibercept (trade name: Eylea; Research Code: AVE-0005, also known as VEGF Trap), a recombinant fusion protein indicated for the treatment of patients with neovascular (wet) age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
AMD is an eye condition which usually occurs in older patients and affects the macula area of the retina, causing loss of vision and eventually blindness. In particular, wet AMD is characterised by an abnormal growth of new blood vessels (neovascularisation) behind the retina. This originates from an abnormal activation of angiogenesis, by the vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A; ChEMBL: CHEMBL1783; Uniprot: P15692) and the placenta growth factor (PlGF; ChEMBL: CHEMBL1697671; Uniprot: P49763), of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptors VEGFR-1 (ChEMBL: CHEMBL1868; Uniprot: P17948) and VEGFR-2 (ChEMBL: CHEMBL279; Uniprot: P35968), two receptor tyrosine kinases present on the surface of endothelial cells. This leads to abnormal increased permeability, scarring and possibly to the loss of fine-resolution central vision. Aflibercept acts as a soluble 'decoy' receptor that binds VEGF-A and PlGF and thereby inhibits the binding and activation of the VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 receptors.
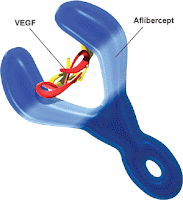
Aflibercept is a recombinant fusion protein that incorporates portions of extracellular domains of the human VEGFR-1 (containing Ig-like C2-type 2 domain fragment; Uniprot: P17948|151-214|) and VEGFR-2 (containing Ig-like C2-type 3 domain fragment; Uniprot: P35968|224-320|) fused to the Fc portion of human immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1). Aflibercept is a dimeric glycoprotein with a protein molecular weight of 97 kDa (115 kDa with glycosylation).
>Aflibercept
SDTGRPFVEM YSEIPEIIHM TEGRELVIPC RVTSPNITVT LKKFPLDTLI PDGKRIIWDS
RKGFIISNAT YKEIGLLTCE ATVNGHLYKT NYLTHRQTNT IIDVVLSPSH GIELSVGEKL
VLNCTARTEL NVGIDFNWEY PSSKHQHKKL VNRDLKTQSG SEMKKFLSTL TIDGVTRSDQ
GLYTCAASSG LMTKKNSTFV RVHEKDKTHT CPPCPAPELL GGPSVFLFPP KPKDTLMISR
TPEVTCVVVD VSHEDPEVKF NWYVDGVEVH NAKTKPREEQ YNSTYRVVSV LTVLHQDWLN
GKEYKCKVSN KALPAPIEKT ISKAKGQPRE PQVYTLPPSR DELTKNQVSL TCLVKGFYPS
DIAVEWESNG QPENNYKTTP PVLDSDGSFF LYSKLTVDKS RWQQGNVFSC SVMHEALHNH
YTQKSLSLSP G
Other therapies to treat AMD are available on the market and these include Verteporfin (ChEMBL: CHEMBL1200573; approved in 2000; trade name Visudyne), Pegaptanib sodium (ChEMBL: CHEMBL1201421; approved in 2004; trade name Macugen) and Ranibizumab (ChEMBL: CHEMBL1201825; approved on 2006; trade name Lucentis).
Aflibercept recommended dosage is 2 mg administrated by intravitreal (into the eye cavity) injection every 4 weeks for the first 12 weeks, followed by 2 mg via intravitreal injection once every 8 weeks.
Following intravitreal administration of 2 mg per eye, a fraction of the administrated dose binds to the endogenous VEGF in the eye to form the inactive Aflibercept:VEGF complex. Once absorbed into the systemic circulation, Aflibercept presents in the plasma as the free unbound Aflibercept and predominantly as the inactive Aflibercept:VEGF complex. Aflibercept has a volume of distribution (Vd) of 6 L and a terminal elimination half-life (t1/2) of 5 to 6 days after iv administration of doses of 2 to 4 mg.kg-1 of Aflibercept. Aflibercept undergoes elimination through both target-mediated disposition via binding to free endogenous VEGF and metabolism via proteolysis.
The full prescribing information for Eylea can be found here.
The full prescribing information for Eylea can be found here.
The license holder is Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and the product website is www.eylea.com.